Introduction to Integrated Freeze Drying Systems
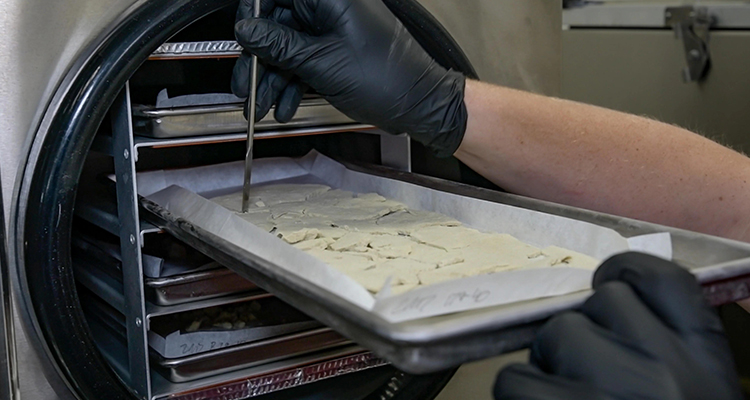
Integrated freeze drying systems, also known as lyophilization systems, are advanced equipment designed to remove water from products through sublimation under controlled low-temperature and vacuum conditions. These systems are widely used across pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and food industries to preserve sensitive products such as vaccines, enzymes, probiotics, dried fruits, and instant coffee. The integration of all freeze-drying stages into a unified system allows for automation, consistent product quality, and compliance with regulatory standards. Sieno Freeze-drying Technology Research Institute (Jiangsu) Co., Ltd. has been at the forefront of integrating freeze-drying science with intelligent equipment manufacturing, providing comprehensive solutions from raw material processing to finished product packaging.
Components of an Integrated Freeze Drying System
An integrated freeze drying system combines primary, auxiliary, and control components into a single unified framework to optimize efficiency and product quality.
Primary Components
- Freeze Dryer (Lyophilizer): Features advanced chamber design, high-quality materials, precise shelving systems, and temperature control to ensure uniform drying.
- Vacuum System: Includes rotary vane, scroll, or diffusion pumps, along with vacuum gauges and precise control mechanisms to maintain low-pressure conditions.
- Refrigeration System: Comprises compressors, refrigerants, and efficient cooling mechanisms, capable of maintaining required temperature ranges for freezing and sublimation.
- Control System: Incorporates PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), HMI (Human Machine Interface), and data logging to monitor and automate the drying process accurately.
Auxiliary Components
- Automated Loading and Unloading Systems: Minimize manual handling and improve throughput.
- Ice Condenser: Efficient design with defrosting mechanisms for effective water vapor capture.
- Nitrogen Purge System: Reduces oxidation risks and maintains product stability.
- Clean-in-Place (CIP) Systems: Automates cleaning and ensures hygienic operation.
Types of Integrated Freeze Drying Systems
Integrated freeze drying systems can be classified based on scale, application, and configuration. Selecting the right type depends on production volume, product characteristics, and operational requirements.
Based on Scale
| Scale | Description | Typical Features |
|---|---|---|
| Laboratory-scale | Small units designed for R&D, product development, and testing | Low volume, flexible trays, experimental control |
| Pilot-scale | Intermediate systems bridging lab-scale results to full industrial production | Medium volume, adjustable shelving, data collection for scale-up |
| Industrial-scale | Large systems designed for mass production | High throughput, continuous operation, robust automation |
Based on Application
| Application | Products | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical | Vaccines, injectables, antibiotics, APIs | Strict sterility, precise temperature and vacuum control |
| Biotechnology | Enzymes, proteins, cell cultures, probiotics | Maintain biological activity and viability |
| Food Processing | Dried fruits, vegetables, instant coffee, tea, dairy products | Flavor, color, nutrient retention, texture consistency |
Based on Configuration
| Configuration | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Automated vs. Manual Systems | Automated systems reduce manual labor and human error; manual systems may be used for small-scale or flexible operations | Automation ensures consistency; manual offers flexibility |
| Batch vs. Continuous Systems | Batch systems process one load at a time; continuous systems allow uninterrupted production for high-volume applications | Batch is versatile; continuous maximizes throughput |
Sieno Freeze-drying Technology Research Institute (Jiangsu) Co., Ltd. provides integrated systems across all these types, combining intelligent control, modular design, and industry-specific customization to optimize performance and product quality for laboratory, pilot, and industrial-scale operations.
Benefits of Using Integrated Freeze Drying Systems
Integrated freeze drying systems offer several advantages including efficiency, quality, cost savings, compliance, and sustainability.
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Throughput
Integrated systems synchronize freezing, primary drying, secondary drying, and unloading under a single control platform, reducing cycle times and manual handling.
| Parameter | Standalone Systems | Integrated Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle time per batch | 24–48 hours | 12–30 hours |
| System downtime | 10–15% | <5% |
| Operator involvement | High | Low |
| Process continuity | Intermittent | Continuous |
Sieno Freeze-drying Technology Research Institute (Jiangsu) Co., Ltd. integrates AI-based scheduling and predictive process control to optimize throughput and dynamically adjust shelf heating and vacuum depth for high-volume operations.
2. Improved Product Quality and Stability
| Parameter | Traditional Freeze Dryer | Integrated Freeze Dryer (Sieno) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature uniformity | ±2°C | ±0.5°C |
| Moisture uniformity | ±3% | ±1% |
| Bioactive retention | 80–85% | 95–98% |
| Product rehydration time | 60–90 sec | 30–45 sec |
Sieno’s adaptive shelf temperature control and vacuum regulation preserve enzymes, probiotics, and food products, ensuring superior quality.
3. Reduced Operating Costs
| Parameter | Conventional Setup | Integrated System (Sieno) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy consumption per batch | 100–120 kWh | 70–85 kWh |
| Labor requirement | 3–4 operators | 1–2 operators |
| Maintenance frequency | Every 2 weeks | Every 4–6 weeks |
| Overall cost reduction | — | 20–30% savings |
Sieno’s heat recovery, variable-speed vacuum, and intelligent energy management optimize operating costs and improve sustainability.
4. Compliance with Regulatory Standards
| Compliance Parameter | Non-integrated Systems | Integrated Systems (Sieno) |
|---|---|---|
| Data logging accuracy | Manual/Partial | Fully automated, 100% traceable |
| GMP validation support | Limited | Complete with documentation |
| Audit readiness | Requires manual preparation | Real-time digital reports |
| CIP/SIP compliance | Manual | Fully automated and validated |
Sieno designs systems with built-in documentation, audit trails, and automated CIP/SIP ensuring full GMP and FDA compliance.
5. Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
| Indicator | Conventional Systems | Integrated Systems (Sieno) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy efficiency ratio (EER) | 2.0–2.5 | 3.0–3.8 |
| Water use per cleaning cycle | 300–500 L | 150–250 L |
| CO₂ emission reduction | — | Up to 25% less |
| Refrigerant type | Legacy R-series | Eco-compatible (low-GWP) |
Sieno integrates heat recovery, smart defrost management, and eco-friendly refrigerants for sustainable operation.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Integrated Freeze Drying System
Choosing the right integrated freeze drying system is critical for efficiency, product quality, and compliance. Key factors include product requirements, throughput, budget, supplier support, regulatory compliance, and automation.
1. Product Requirements
Consider thermal sensitivity, moisture content, particle size, and oxygen sensitivity.
| Product Type | Freeze Temperature | Primary Drying Pressure | Residual Moisture Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat-sensitive proteins / enzymes | −50°C to −55°C | 0.05-0.1 mbar | <2% |
| Probiotics / live cultures | −45°C to −50°C | 0.05-0.2 mbar | <3% |
| Dried fruits / tea / coffee | −40°C to −50°C | 0.1-0.5 mbar | 1-3% |
Sieno conducts detailed product analysis and applies precise shelf temperature and vacuum controls to preserve quality.
2. Capacity and Throughput Needs
| Metric | Pilot Scale | Industrial Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Shelf area | 1-5 m² | 10-50+ m² |
| Conden ``` ser ice capacity | 20-80 kg | 200-1000 kg |
| Number of cycles per week | 5-10 | 20-50+ |
| Output per week | 100-500 kg | 1-10+ tons |
Sieno provides modular pilot and industrial solutions to match throughput requirements efficiently.
3. Budget and Total Cost of Ownership
| Cost Element | Lower-Cost Setup | Integrated High-Automation Setup |
|---|---|---|
| Capital investment | Lower upfront cost | Higher due to automation, CIP/SIP, advanced control |
| Energy consumption per batch | Higher | Lower, energy recovery optimized |
| Labor requirement | High | Reduced |
| Maintenance frequency | Frequent manual servicing | Planned preventive and predictive |
Sieno’s Value Proposition
Sieno Freeze-drying Technology Research Institute (Jiangsu) Co., Ltd. invests in integrated system features that may cost more initially (automated loading, CIP, precise refrigeration & vacuum control) but reduce long-term costs significantly. Their intelligent energy management, predictive diagnostics, and modular design help clients lower energy bills, reduce maintenance downtime, and achieve faster return on investment. Sieno’s systems are designed to balance upfront expense with long-term efficiency and durability.
4. Supplier Reputation, Support, and After-Sales Service
An integrated freeze drying system is a complex investment; supplier capability, support, and reliability are crucial.
Support Aspects to Evaluate
- Expertise in freeze drying science and control engineering
- Ability to customize solutions for your product types
- Availability of technical service, spare parts, preventive maintenance
- Support for validation, regulatory documentation, operator training
Parameter Comparison
|
Support Metric |
Typical Small Vendor |
High-Reputation Specialized Provider (like Sieno) |
|
Customization of drying cycles |
Limited |
High – tailored per product, collaborative R&D |
|
Technical support response time |
Slow / variable |
Fast, dedicated, possibly remote diagnostics |
|
Spare parts availability |
May be limited |
Readily available, standardized modules |
|
Validation / regulatory support |
Basic |
Comprehensive – includes documentation, compliance support |
5. Regulatory Compliance
Depending on your industry (pharmaceuticals, food, biotech), you need to ensure your system meets relevant regulations and standards.
Relevant Regulatory Aspects
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP)
- FDA / EMA regulations for pharmaceuticals and biologic
- Food safety standards (HACCP, ISO etc.)
- Data integrity (21 CFR Part 11, data logging, audit trails)
- Hygiene standards (clean-in-place, sterile design, purification of purge gases)
Parameter Comparison
|
Compliance Feature |
Minimal System |
Fully Compliant Integrated System |
|
Sterility / Cleanliness |
Basic; manual cleaning, open chamber |
CIP / SIP, HEPA filtration, isolated loading |
|
Data Logging / Traceability |
Manual or semi-automated logs |
Automated, digital, tamper-proof logs with audit trail |
|
Documentation for Validation |
Required but may be generic |
Detailed, product-specific, includes IQ/OQ/PQ |
|
Use of Purge Gas (e.g. Nitrogen) |
Optional / limited |
Integrated, high-purity, programmable |
6. Technology and Automation Features
The degree of automation, control, and “smart” technology can significantly impact performance, consistency, and ease of operation.
Features to Look For
-
Programmable recipes for different products
-
HMI with process visualization and remote monitoring
-
Predictive maintenance / alarms
-
Adaptive algorithms for temperature, pressure, and shelf heating based on real-time data
Parameter Comparison
| Feature | Basic Systems | Advanced Integrated Systems (Sieno Level) |
|---|---|---|
| Recipe control | Manual or few presets | Extensive product libraries, user-customizable |
| Remote monitoring | Rare or basic | Full remote access, dashboards, alerts |
| Predictive maintenance | Reactive repairs | Scheduled and predictive, analytics-based |
| Adaptive control | Fixed profiles | Real-time adjustments (temperature, vacuum, shelf heating) |
 English
English  русский
русский  中文简体
中文简体 















































 +86- (0) 519-8578 6988
+86- (0) 519-8578 6988  +86-180 6875 7376
+86-180 6875 7376  emmy@jsblk.com
emmy@jsblk.com  Zhenglu Town, Tianning District, Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province, China
Zhenglu Town, Tianning District, Changzhou City, Jiangsu Province, China